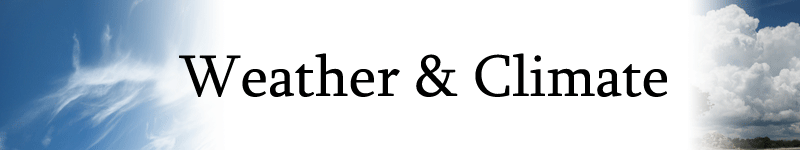
Weather is the short term conditions of the atmosphere around us, whereas climate is the longer term average conditions of a place.
Weather Conditions |
Instrument |
Measuring Unit |
Rainfall |
Rain Guage |
mm |
Air Pressure |
Barometer |
mb |
Humidity |
Hygrometer |
% |
Wind Speed |
Anemometer |
Km/hr or Miles/hr |
Wind Direction |
Weather Vane |
Compass directions |
Temperature |
Thermometer |
Degrees C or F |
Types of Rainfall
Convectional Rainfall
- This happens as the sun heats the earth. The earth heats the air above it which causes it to start rising. As it rises it cools, condenses and rains.
- On a sunny day clouds often form in the afternoon due to this process and can lead to heavy downpours.
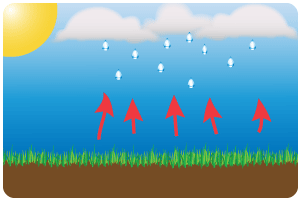
Relief Rainfall
- This is caused by physical features causing the air to rise.
- Mountains cause the air to rise, it cools and condenses. They often have clouds around the tops and have higher rainfall totals.
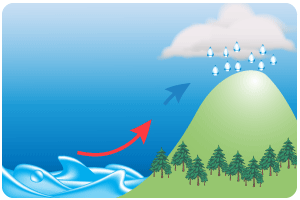
Frontal rainfall
- This occurs when two air masses meet. The warmer air mass rises above the cooler one.
- As it rises it cools and condenses and then rains.
- Common in the UK where there are several air masses often meeting.
Factors Affecting Climate
Solar Radiation Received
-
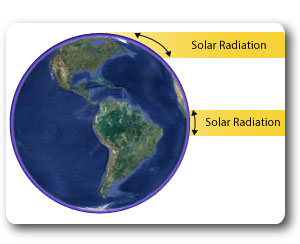
The concentration of the suns energy reaching the earth diminishes with distance from the equator. As the diagram shows, the curvature of the earth results in the solar radiation being spread over a much wider surface area at higher latitudes.
The result of this is much warmer temperatures around the equator which results in high levels of evaporation from the oceans.
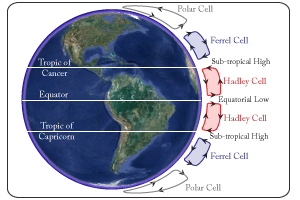
Atmospheric Circulation
- Equatorial low: low pressure surrounding the equator. This is where tropical rainforests exist.
- Sub-tropical high: high pressure areas around the tropics of Cancer & Capricorn. This is where the major deserts of the world exist.
- These air cells redsitribute heat around the globe through moving warmer air from the equator north & south, and colder air from the poles towards the equator.
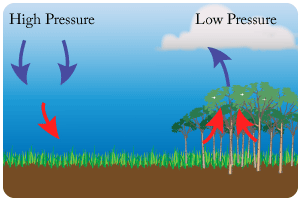
Air Pressure
- Low pressure = rising air. This happens around the equator due to the strength of the sun. It creates a lot of cloud and rain, often unstable weather conditions.
- High pressure = descending air. As it descends it warms up. It brings clear skies and sun. This happens around 25 degrees North and South of the equator and creates deserts.
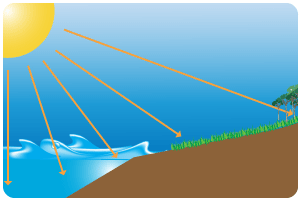
Distance from Coast
- Sunlight warms only the top layer of the earths surface whereas in the oceans the sunlight penetrates much deeper. Because of this the land heats up quicker in the Summer month than the oceans. In Winter though, the land looses its heat much faster.
- Coastal climates are likely to be warmer in Winter and cooler in Summer than continental locations.
Climate Graphs
The Greenhouse Effect
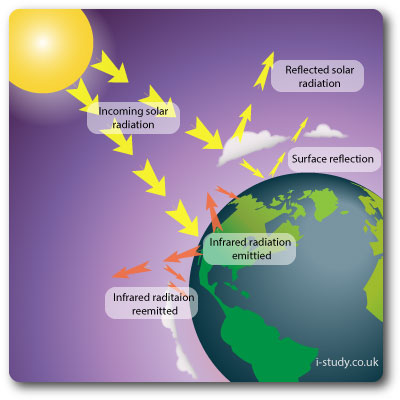
Incoming solar radiation enters the earths atmosphere. Some is reflected by clouds and some more is reflected by atmospheric pollution.
On reaching the earths surface some of the light is reflected depending on the albedo rate (ice sheets, oceans etc).
The rest is used by plants (photosynthesis) or absorbed by the land and oceans. This heats the land and oceans with the heat being released into the atmosphere as longwave infrared radiation.
The greenhouse gases trap some of this infrared radiation in the atmosphere. Increasing levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increase the amount being re-emitted back in the atmosphere.


