

Globalisation
“The growing interdependence of countries worldwide through the increasing volume and variety of cross-border transactions in goods and services and of international capital flows, and through the more rapid and widespread diffusion of technology” (source: IMF).
The KOF Index
Objective: Be able to describe how the KOF index is calculated and its spatial representation.
Tasks
Friction of Distance
What is Time-Space Convergence?
The reduction in the time taken to travel between two places due to improvements in transportation or communication technology.
Over the last century travel times have reduced drastically as the supply of and demand for commercial flights has boomed.
On a more local scale, car ownership has also drastically increased, roads have been improved and vehicles have got faster & more efficient.
BBC article - looking at aspects of the shrinking world & timescales
Friction of Distance
This is based on the idea there are obstacles or barriers that make travel more difficult (friction).
The longer the journey – generally the more friction & so we make longer journeys less frequently.
Reducing the Friction of Distance
Developments in transport have:
These developments have reduced some of the friction of distance & led to time-space convergence.
Changing Notion of Distance
These developments are changing the way we think about distance & travel.
The time it takes to get to a place is now often more important/significant than the actual distance it is.
In this sense, since travel times have decreased, places have essentialy become closer – the world has shrunk!
Its not just in the transportation of people that we have the effect of a shrinking world. Goods and services are also experiencing this.
Containerisation
Containerisation has revolutionised the way that goods are transported and been one of the main factors in the emergence of global supply chains.
Growth of the Internet & the Digital Divides
What is the Internet?
You should have an understanding of what the internet actually is, and its reliance on a physical infrastructure.
The physical infrastructure and its cost of installation is a major factor in disparities of access to the internet on a variety of scales (global, regional and national).
Digital divides often exacerbate inequalities in wealth.
Global Internet Connections
Use figure or click on the link under the image ot be taken to the full size version at source to answer the following.
Digital Divides
•Despite the internets rapid emergence as a global communication tool it is still out of reach of many of the worlds population.
•The expensive infra-structure needed to provide fast broadband has led to richer countries leaping ahead in the digital world.
•Mobile phone technology & coverage is rapidly improving but many phones cannot access the internet & the cost is high & phones screens are generally too small
The digital divide- Mexico (Guardian 2011)
East Africas Internet Revolution
Tasks
Read & make notes about the new connection to East Africa: East African fibre-optic connection (Guardian2008)
(Which countries will it benefit, hoped impacts on businesses, people & education).
What are the problems for countries that rely on satelites providing poor connections.
Broadband increases in Africa & the potential of satelites to deliver broadband, BBC article 2012
National Divisions: Rich-Poor
A trend is emerging in both rich & poor countries in relation to internet access/use.
The cost & commitment of monthly payments for broadband provision is meaning:
Income & education levels are creating a digital divide. The UK digital divide - factfile
National Divisions: Rural-Urban
•Urban areas have much higher proportions of people connected to broadband services & offer much faster speeds. The cost of installing the cables has meant rural areas rely on:
•This is an issue that is affecting MEDCS & LEDCs.
•Private companies are profit motivated & less likely to invest heavily in small rural connections
Rural broadband: digital divide is widening (Telegraph 2010)
Organisation Involved in Transfers of Capital
There are various forms of capital transfers on a global scale:
You should have an understanding of the role of the following institutions/organisations in financial flows (and loans): IMF, World Bank, WTO.
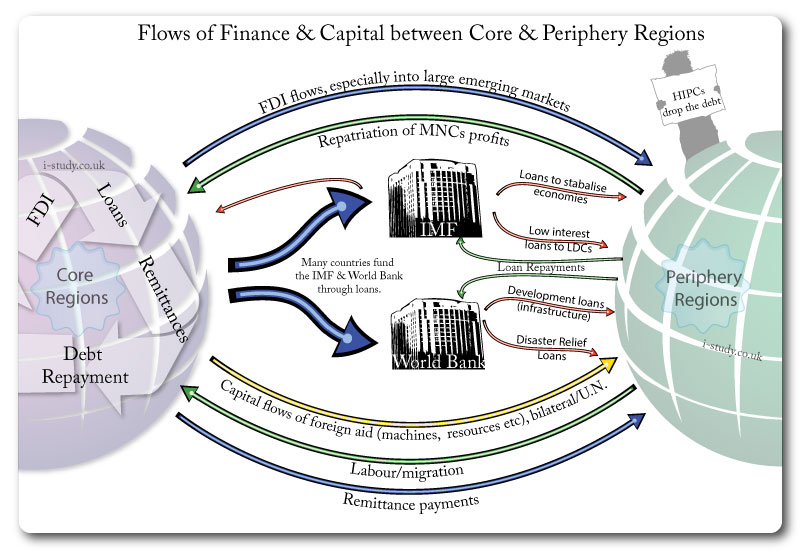
The World Bank
The International Monetary Fund (IMF)
The World Trade Organisation
1) Read this BBC article & make notes about what the WTO is & what it does. 2) What are the criticisms of the WTO?
Repatriation of Profits
Global Remittances
These are flows of money sent back by migrants to their home country.
Remittances go directly to the intended recipient and can be used how they choose to improve their quality of life (rather than through governments or agencies).
High fees unfairly penalise the poorest workers. Migrants sending small sums of money home get charged the highest %s. Also sending money to the poorest regions (African countries) also often carry higher fees.
Tasks
Global Outsourcing
Objective: be able to describe patterns of global outsourcing and suggest reasons for the top outsourcing destinations. Be able to explain the role it plays in global transfers of capital.
Tasks
Case Study: Bangalore, India
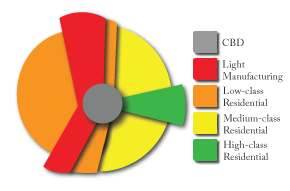
Concentric Ring Model
Food Miles
Tasks
Agro-Industrialisation
Modern food production systems are being increasingly industrialised. Increasing the scale of production, mechanising many of the processes, increasing efficiency and using scientific techniques are reducing the cost of food.
Whilst the monetary cost of production may have fallen, the cost to the environment has been increasing:
Negative Impacts of Agro-industrialisation
Tasks
Benefits of Agro-industrialisation
Despite the many negative impacts on the environment that the industrialisation of food production has caused, there are also many opportunities for it to actually be of benefit.
Tasks
Trafigura, Ivory Coast
Union Carbide; Bhopal, India
Tasks
Chernobyl Nuclear Accident
Objective: describe one major pollution event affecting more than one country and examine the consequences of and responses to this event.
Tasks
Cultural Diffusion
Objective: Describe cultural traits in terms of language, customs, beliefs, dress, images, music, food and technology.
Read: A good introduction to culture and cultural steroetypes & diffusion
Americanisation Vs Globalisation
Objective: describe the role of TNCs and the media in spreading consumer culture. Select two different branded commodities and examine the spatial and temporal pattern of adoption on a global scale.
Americanisation or Globalisation?
KFC in China (2012)
McDonalds Global Spread
Tasks
Use the link below and the infographic opposite to make Case Study notes about:
Starbucks Global Spread
Tasks
Starbucks spread their coffee culture in China
The Coffee empire
A business needs to have plenty of competitive advantages to become an empire.
First, Starbucks directly controls every important step of its business, from buying high-quality coffee beans to designing its franchise decor. This allows Starbucks to minimize its operating risks. For example, by being one of the most important buyers of coffee arabica in the world, the company has enormous influence over its suppliers and it can ensure competitive prices, superior quality, and the necessary quantities at the right time.
Second, Starbucks creates a unique atmosphere surrounding its products based on four key factors: quality, service, ambiance, and culture.
The company maximizes quality not only by buying high-quality coffee beans, but also by equipping its coffee houses with excellent coffee machines.
To ensure perfect service, the company trains its baristas for over 30 hours. Baristas become very professional, not only at making coffee, but also at handling as many as 200 customers per hour.
In terms of ambiance, Starbucks has carefully chosen its color combination, couches, and lights to create a great place for coffee-lovers. The company keeps its customer loyalty high by promoting a genuine passion for coffee that goes beyond a cup of cappuccino. Starbucks promotes coffee rituals, love for organic ingredients, environmental friendship, and millennial values.
Finally, Starbucks is constantly innovating its menu and starting new businesses, such as selling energy drinks or coffee machines. The company has recently focused on strengthening its sandwiches and bakery business. That's why last year the company shelled out $100 million to acquire La Boulange Bakery, which specializes in traditional pastries. More recently, the company launched a £2 breakfast offer in the U.K. to capture price-sensitive customers.
source: http://www.fool.com/investing/general/2013/10/26/how-starbucks-built-a-coffee-global-empire.aspx
Diasporas
Diasporas: the dispersal of a population away from their homelands. It may be forced or voluntary.
Italian diaspora in New YorK
Between the late 1800s and the early 1900s millions of Italains migrated to the United States. Poverty in Italy and the notion of opportunity in the US drove this large scale migration.
The cultural impact of this Italian diaspora can still be recognised in the culture of modern day New York. The Italians established communities and retained their traditional customs of which some became part of the wider society.
Tasks
Use this link to answer the following questions
Read the "Life in a New World" section on this page.
Indian diaspora in the UK
Tasks
Cultural Imperialism
Cultural Imperialism the promotion of a countries culture onto another country.
Cultural imperialism has occured throughout history. Early civilisations as the expanded actively imposed their cultures on the the new regions that they controlled. The Roman empire imposed language, cuisine, and architecture as it expanded throughout Europe.
More recently the British and Spanish empires practised cultural imperialism on their colonies.
Australia and New Zealand retain many traits of the UK and still have strong political links. Rail networks were installed in many colonial African countries and through India. English is also widely spoken in many parts of India.
The Spanish empire resulted in Central America speaking Spanish, having similar traditional dance styles and costumes.
The last century has witnesssed the global dominance of certain brands and they have played a role in promoting cuisine, music and dress in other countries.
McDonalds, Coca Cola, Nike have actively promoted American styles and tastes in foreign places, not just through their products but also through the style/music of their adverts. In recent years they have been making more effort to adapt their producst to reflect the cultural traits of the countries that they operate in.
Globalisation has enabled companies to sell to global markets, vastly increasing their customer base both in actual numbers and geographical locations. This expansion has generated enormous profits for a number of companies with many of them generating more revenue than entire countries.
Tasks
E.U. Case Study
Syllabus requirement: Discuss the links between the diminishing effectiveness of political borders and the flow of goods, capital, labour and ideas, and the role of one multi‑governmental organization such as the European Union (EU)
Tasks
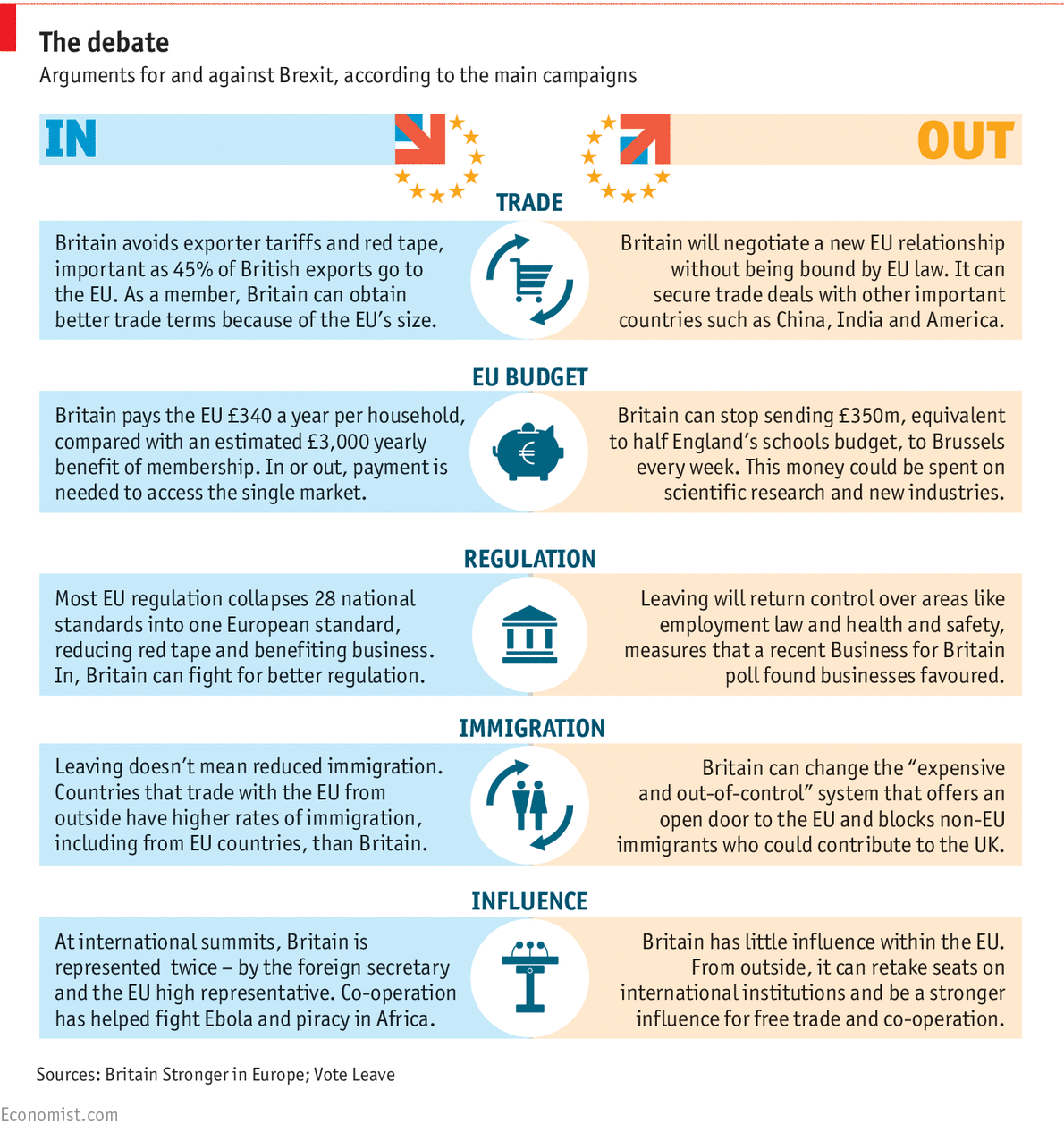
Responses to Loss of Sovereignty
Syllabus requirement: Examine the resurgence of nationalism in one country as it attempts to retain control of its resources and culture.
Neo-nationalism & the EU
Anti-globalisation
Tasks
The start of this century has witnessed an increasing concern about the impact of globalisation, particularly in relation to inequality, the power of MNCs and the environment.
Protests have accompanied most meetings of world leaders, particularly in relation to the WTO, IMF and World Bank. The internet and social media are enabling these protests to take on global dimensions and significance with large scale, international co-ordinated gatherings/actions.
Watch Videos to the right and complete the tasks below.
Voices of protest (2012)
Migration Control: United States
Tasks
Good review of migration control
Read this article & make notes about:
Read this article and describe the methods being used to control Mexican immigration into the USA through the land border.
interactive chart showing data about border control
Using the information from this graphic discuss the reasons behind the control of the border. Do you think it is mainly to stop illiegal workers or is the drug trade a big factor?
Glocalisation
Defnition: A term that was invented to emphasize that the globalization of a product is more likely to succeed when the product or service is adapted specifically to each locality or culture in which it is marketed.
Tasks
Read through gthe following articles and make notes about the ways in which firms glocalise their products and the motivations behind these strategies.
BBC: Glocalisation and the adaptation of webpages to local audiences
BBC 2013: Multinationals & adapting to local working customs
McDonalds
The increasing presence of McDonald’s restaurants worldwide is an example of globalization, while changes made to the menus of the restaurant chain, in an attempt to appeal to local tastes, are an example of glocalization.