

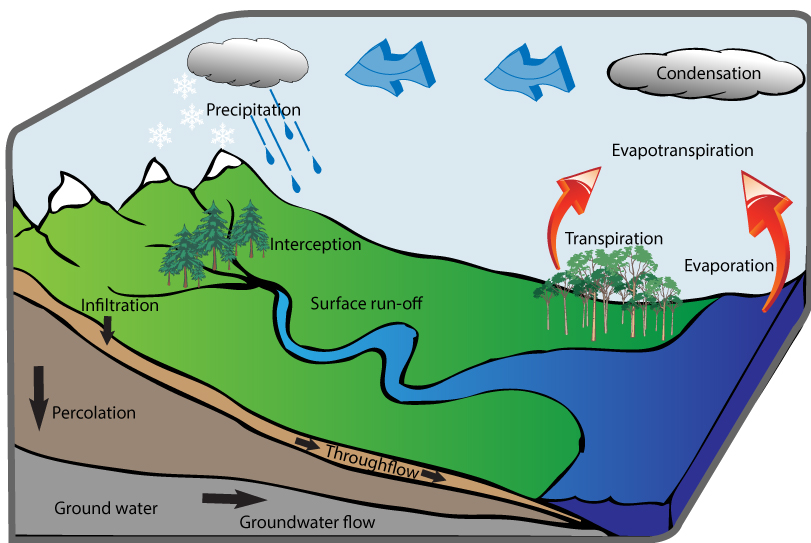
Hydrological Cycle
Water balance: relationship between inputs and outputs of a drainage basin.
Precipitation = Q (runoff/discharge) + E (evapotranspiration) +/- changes in storage.
Tasks
1. Define the different stages in the hydrological cycle:
2. Identify stores (groundwater, lakes, clouds) and transfers (precipitation, evaporation, throughflow etc).
Changing Balance of Ice and Water
Climate change is reducing the volume of water stored as ice.
Tasks
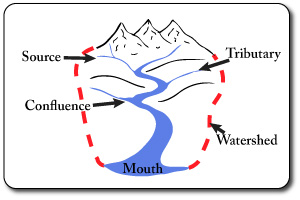
Drainage Basin: The area drained by a river and its tributaries.
Drainage Divide: Also known as a watershed, it is the line defining the boundary of a river or stream drainage basin separating it from adjacent basin(s).
You should have an understanding of the following river features:
*source, tributary, confluence, channel, floodplain, mouth, delta, distributaries.
* River profile & characteristics: upper, middle & lower valley. Bradshaw model. Waterfalls.
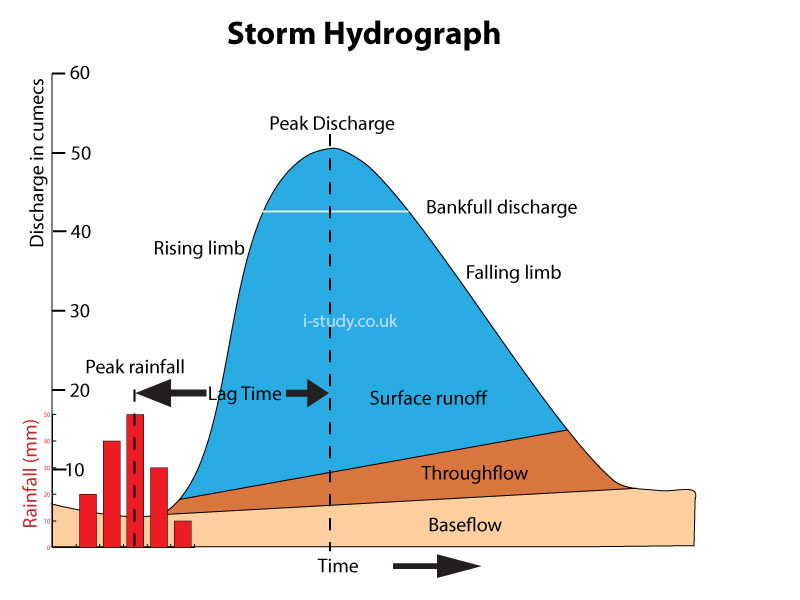
* River discharge: define, measurement (cumecs).
The Bradshaw Model
Figure A3: Bradshaw model shows how rivers change as they move from the source to the mouth. Study the model and make sure you can explain why some factors increase while others decrease with distance from the source.
River profile & characteristics: upper, middle & lower valley. Bradshaw model. Waterfalls. River discharge: define, measurement (cumecs).

Tasks
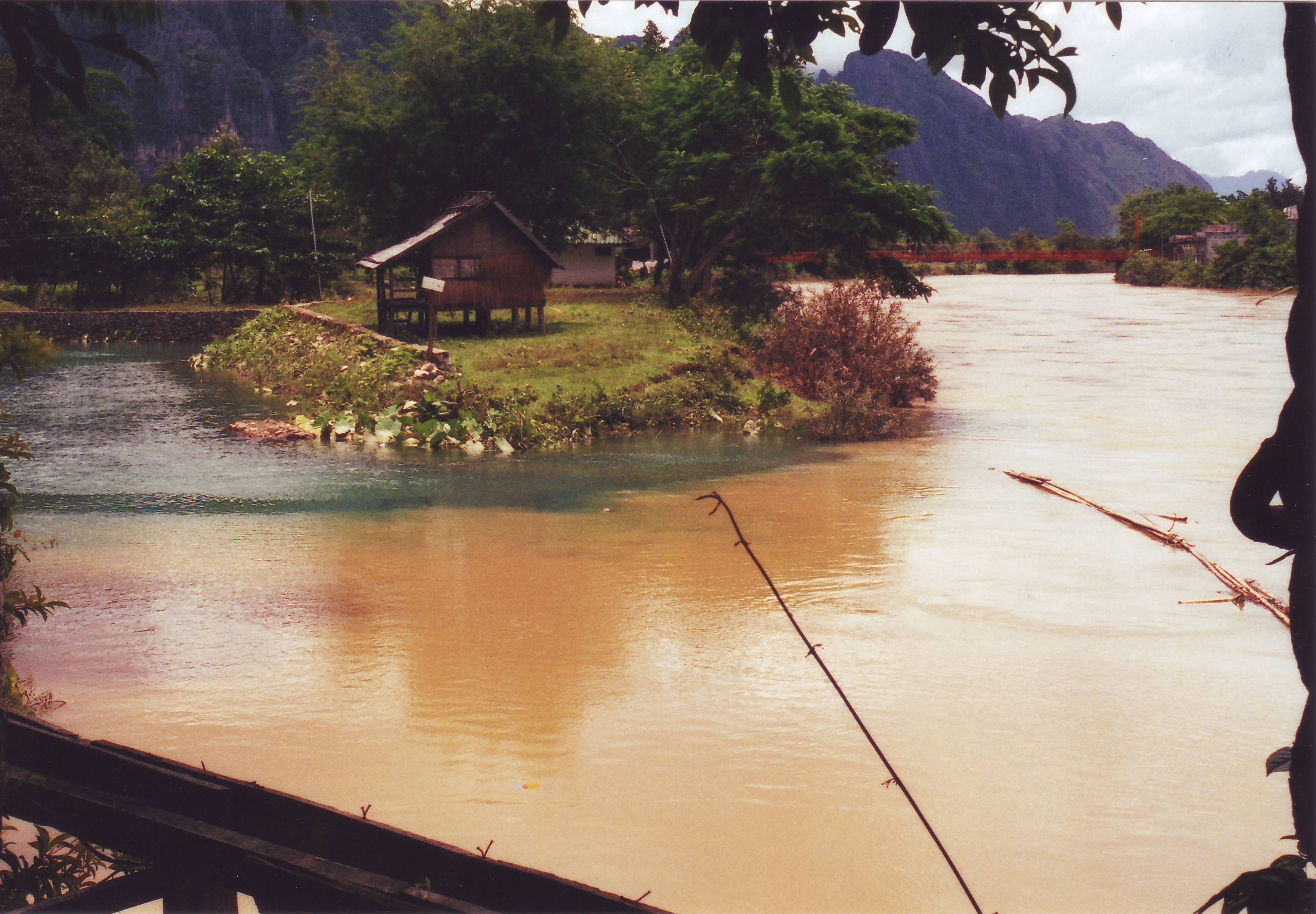
Pakistan Floods 2010
Flooding is the most obvious and devastating hazard of living close to rivers. Pakistan experienced severe flooding in 2010 that displaced millions of people.
Tasks
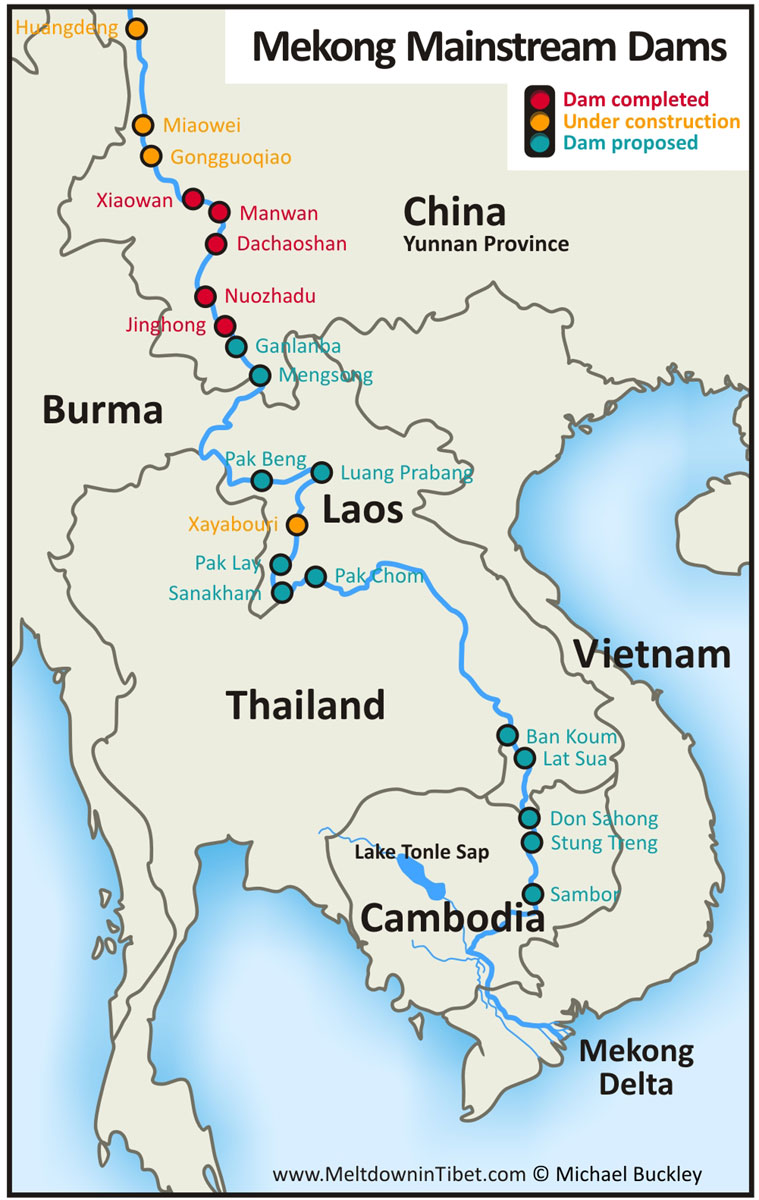
Damming the Mekong
Tasks
Open this Guardian article about the Mekong
Create a Case Study about the environmental and human impacts of economic development and the Mekong River:

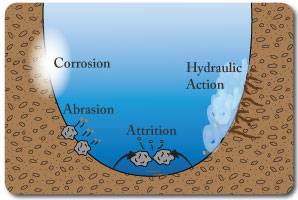
Erosion
You should be able to explain where these erosional processes take place eg: attrition and abrasion occur largely in the upper course where the larger more angular rocks scrape and collide when they move.
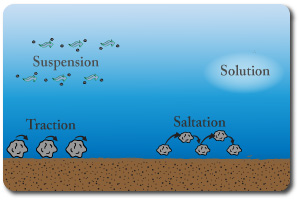
Transportation
You should be able to describe the changes in the typeof transportation that occur with distance from the source.
Water Extraction
Maximum Sustainable Yield: Maximum Sustainable Yield: The maximum level of extraction that can be maintained indefinitely for a given area.
Read this article for an introduction to the unit Groundwater. Published by http://www.yearofplanetearth.org/
Tasks
Case Study: Kissimmee River Restoration
Wetlands: Areas that are regularly saturated by surface water or groundwater, including freshwater marshes, swamps and bogs.
Wetlands are an important ecosystem supporting a wide species diversity. They also filter water passing through them removing many pollutants. In addition they can play a significant role in reducing flood risk.
Many wetland systems around the world are under threat due to development.
Tasks
Additional Resources:
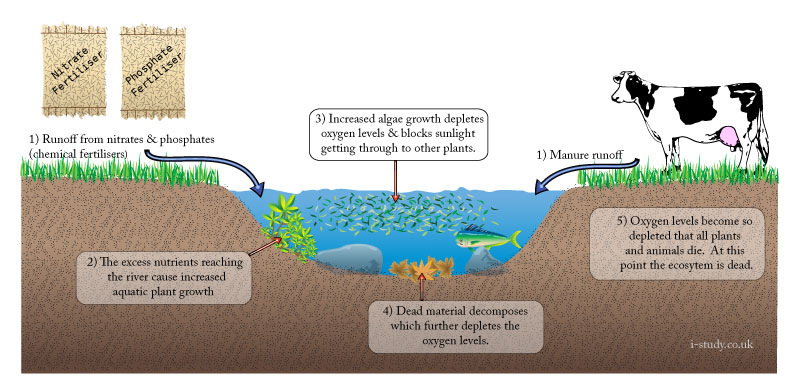
Eutrophication
Eutrophication: nutrient enrichment of streams, ponds and groundwater.
Read this article: Fertilisers: Enriching the worlds soil
Tasks
Conflict in The Andes, Peru
The Guardian.co.uk - The Andes
Mini-series looking at water shortages in Peru. Watch the 3 videos (A7 to A9).
Tasks
The Andes: Retreat of the glacier
Water wars come to Peru
Conflict over the River Nile
The Nile flows through many African countries ending in Egypt at the Nile delta. Egypt is almost completely reliant on the Nile as a source of freshwater due to its desert climate.
Most of the countries it flows through are experiencing rising populations and the need to grow more food. Their economies are slowly industrialising and require more electricity. These factors are resulting in more water being demanded from all the countries which is leading to conflict.
Tasks
The Nile River Basin