
Clasifications
- Primary Industry: Extracting raw materials (fishing, mining, farming).
- Secondary Industry: Manufacturing & construction (making things).
- Tertiary Industry: Service provision ( teachers, bankers).
- Quaternary Industry: Research & Development
(high-tech, I.T. & pharmaceutical).
The proportions of each of the sections that make up a total economy is known as the employment structure.

LEDCs
- Typically have large primary industries & low manufacturing/tertiary & quaternary industries.
- Primary industries require labour but little capital investment and low educational levels.
- Primary product can generate export earnings.
- Setting up manufacturing & services requires large capital investment and a skilled labour force.
MEDCs
- Tend to have small primary sectors & larger secondary & tertiary industries.
- Primary industries are highly mechanised and require a very small labour force.
- Raw materials are often imported for manufacturing.
- Services have become increasingly important as the IT sector has grown..

De-industrilasation of MEDC Economies
Most developed countries have experienced a decline in their secondary industries, particularly heavy manufacturing. Competition from developing countries has led to some firms closing as they can't compete with the lower labour costs in LEDCs. Other firms still remain but have relocated their factories to developing countries. They do this for several reasons:
To be closer to the raw materials, or closer to cheaper sources of raw materials. Resources have been depleted in many developed countries and where they remain, the costs of extracting them is often high.
To benefit from cheaper labour costs. They may also take advantage of less labour laws and the willingness of people to work longer hours and have less holiday days per year.
To be closer to large markets to sell their products. Increasing wealth in many developing countries with large populations (China, India, Indonesia etc) is changing the gobal market place. Many European car manufacturers sell rapidy increasing numbers of their vehicles in China and India.
Decentralisation of Industry
Many industries in MEDCs have become much more geographically mobile. They can locate in a range of places since they are less dependent on raw materials and more dependent on skilled labour.
Many offices and ICT software/hardware companies locate on the edges of urban areas in much more pleasant surroundings. A similar trend has occured with the retail sector as shopping malls in increasingly common in the suburbs of large urban areas.
These locations are often cheaper, have plenty of space for parking and are closer to the workers/customers homes. The development of the internet has rreduced the need to be near services such as post offices, banks and other firms. Email, video conferencing, online banking and similar services allow firms to locate in more rural settings.
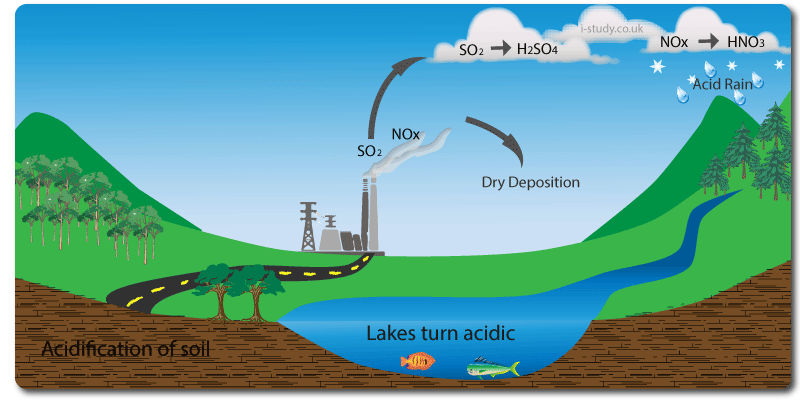
Acid Rain
Links
Interactive graphic comparing the carbon footprints of Innocent & Coke
chocolate consumption by brand
Case Studies
Manufacturing------------------ Secondary Industry----------------------------Nissan
Location: Sunderland, N.E England.
Reason: skilled labour force & high unemployment. Lots of flat land at a low cost (need land for factory, testing & storing cars).
Transport links: A1 motorway linking to London. Close to port to export to Europe. Near Newcastle airport.
Incentives: Government grants & tax reductions for first few years. Ancillary firms located close by.
High-tech Industry---------------Tertiary Industry---------------------M4 Corridor
Location: Along M4 motorway (London-Bristol), Southern England.
Reasons:
- Close to Heathrow (international airport) - import/export & travel.
- Large market close by (London). M4 is excellent road link to London, Oxford, Bristol.
- Close to Oxford University (bright graduates & research facilities).
- Attractive environment which attracts workers (Cotswolds, Chilterns).
- Proximity to similar industries for sharing ideas & integration.
- 2010 News article about M4 corridor


