

Sole Trader
A business that is owned by a single person is known a sole trader business. The owner may employ other people to work in the company but they have no ownership of the firm. Usually small in size and has low set up costs.
Typical examples are plumbers, electricians and gardeners.
Benefits
Disadvantages
Partnership
These are companies that have 2 or more owners (partners) and usually not more than 20. Common examples of partnerships may are dentists, accountants, solicitors and doctors practices.
Benefits
Disadvantages
Private Limited Company (Ltd)
Private Limited Companies are owned by several people through the sale of shares. The shares are not available to the public through the stock exchange, but sold privately to friends and family. Private Limited companies must publish annual reports for their shareholders giving details about the company’s performance.
Advantages
Disadvantages
Public Limited Company (Plc)
Public Limited Companies are listed on a stock exchange and their shares are available for anyone to buy through a stockbroker. They are often relatively large in size.
To become a Plc, the company must publish information about its operations and accounts in a prospectus to inform any potential investors about the company, its direction and financial health. Each year reports must also be sent to all its investors about the previous year’s performance, accounts and future direction.
Advantages
Disadvantages
Cooperative
These are organizations that are owned jointly by their members and run in the members’ interests. There are several types of co-operatives:
Trading co-operatives
Formed when a group of producers team up to become a cooperative. This is common in agriculture; coffee farmers may form co-operatives to share equipment (reduce costs) and to have more influence in the market place due to controlling a larger supply.
Consumer co-operatives
They buy in bulk to benefit from reduced prices, this is then passed on to their members as cheaper prices.
Public Corporations
These are government run organizations and tend to be large in size. They are funded by the government and are not profit orientated. Their main aim is to provide the best service to the public. Utility and train operations are often state run (nationalized), in the UK the BBC (British Broadcasting Corporation) is a public corporation.
Advantages
Disadvantages
Electronics Manufacturing, China
(Clip taken from the video: Manufactured Landscapes)
Car Manufacturing: Mini, Oxford
BMW are one of the worlds major car manufacturers and produce many of their cars in developed countries where wages are high.
Fixed Costs
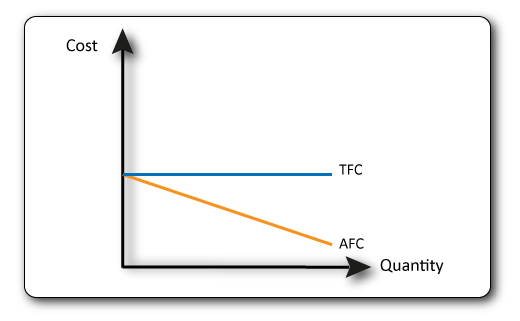
These are the costs that don’t vary with output such as rent, interest on loans etc. This means that the Total Fixed Cost (TFC) line is straight.
The Average Fixed Cost (AFC) line is sloped. TFC/output = AFC. If fixed costs are $10 and 1 item is produced then the AFC is $10, however if 2 items are produced then the AFC is $5.
Variable Costs
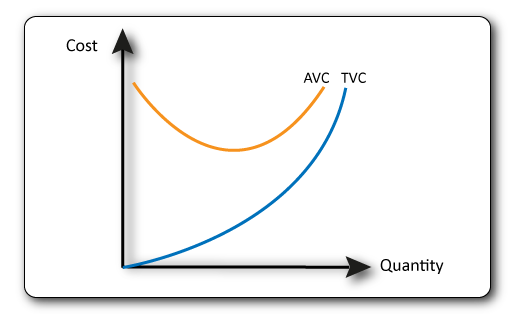
These are the costs that change as output changes such as raw materials, wages, utility bills. As output increases Total Variable Costs (TVC) increase.
Average Variable Costs (AVC) initially fall as productivity of workers increase and the firm benefits from economies of scale but these diminish & may reverse with increased output. TVC/output = AVC
Total Costs
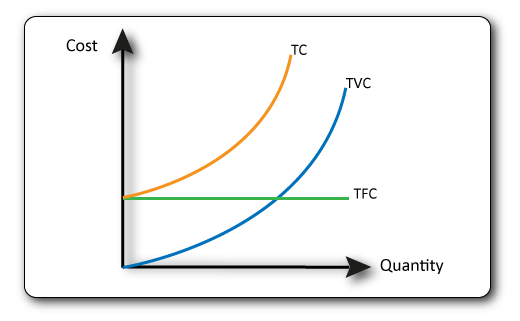
Fixed Costs + Variable Costs = Total Costs.
The total cost line starts at the level of the fixed cost line since these costs must be paid despite no production.
Revenue
Revenue: This is the total amount of money a firms recieves from selling goods (before costs are deducted).
Average Revenue: Total revenue/output
Productivity
The output per worker is known as productivity.
Firms aim to maximise the productivity of their workers in an effort to increase profits. There are several ways in which they may aim to achive this:
Diminishing returns to labour
Increasing the labour force can initially bring increased productivity as many jobs are made quicker through specialization. There are limits though to these benefits and at some point adding additional workers will lead to decreases in productivity.
If workers get in each other’s way, have to wait for shared machinery or cannot communicate effectively, their productivity will diminish, this is known as the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns.
Perfect Competition

Monopolies
Monopoly situations occur when there is a single firm that is the sole supplier. In some cases it makes sense to have a single supplier since duplicating the infra-structure would be inefficient and wasteful. These industries are known as natural monopolies and include water companies, some rail companies (if they own the track) and electricity suppliers.
Characteristics
Monopolies might have complete control over the supply and therefore be able to set prices, but they cannot control the demand. This leaves them with an important choice. They can either:
Disadvantages of monopolies