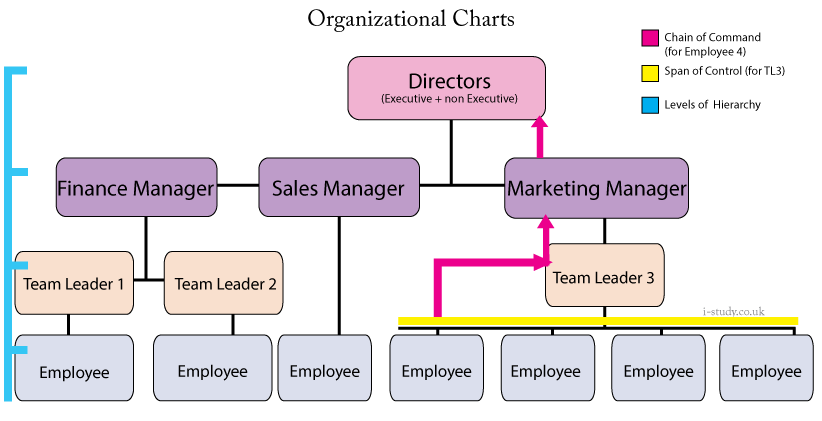
Business Organisational Structures
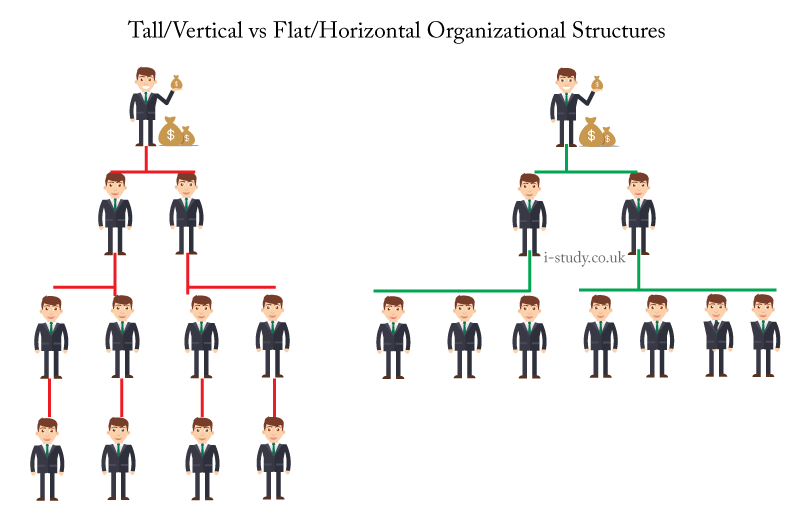
Advantages of a Tall Model:
- Can be more specialised to certain tasks
- Allows for a greater degree of control from team manager
- Commuincation can be filtered as and when neccessary.

Advantages of a Flat Model:
- Allows director to be more involved in every day decision making
- Communication flows quickly and more efficiently
- May improve productivity through greater feeling of unity
Manipulating the Organisational Stucture
Centralisation - this occurs when the span of control is reduced. The organisational structure will therefore become taller. Decentralisation is the opposite
Delayering - this occurs when a company believes it has too many managerial layers and decides to improve efficiency and commuication by removing one of the layers. It may lead to more work for the remaining workers though. This will result in a shorter organisational structure
Delegation - passing down authority from one manager to a subordinate
- Increased participation / motivation
- Less produc
a
Motivational Theory
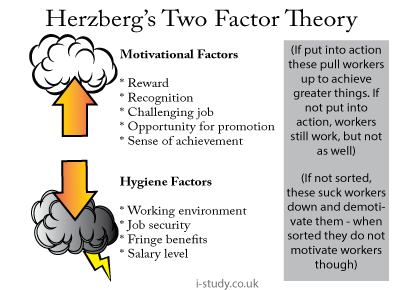
Herzberg's Two Factor Theory
Herzberg's theory differentiates between two separate groups; motivators and demotivators (which he calls Hygiene Factors). If a company had fantastic hygiene factors (such as job security) this does not mean they are motivated to work hard; however, if they do not look after the hygiene factors, then they will be demotivated and produce much less.
On the other hand, motivational factors are independant from hygiene factors; by rewarding workers, challenging them and giving them recognition for their efforts, they will be motivated to work harder and produce more. Motivational factors are not related to salary.
McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y
| Theory X Managers | Theory Y Managers |
|
|
Leadership Types
There are three main forms of leadership:
1) Autocratic - this is when a leader has a high degree of control and imposes his/her will on the workforce. They allocate work to be done, make all major decisions and do not tolerate other ideas. Work is focused and often broken up into componants.
2) Democratic - this occurs when a leader takes the ideas of others around him/her. Decision making is often shared and there is a high degree of delegation. Often associated with a more hands-off laissez-faire attitude.
3) Paternalistic - is the type of leader who listens to other opinions but ultimately makes final decisions, offering advice and guiding the workforce to act in a certain manner.