

Government Objectives
We can identify five main government objectives when discussing the economy. The
economy refers to the activity of all businesses within a country and can be manipulated
by the government. Indeed, the government's aims are:
1. Economic Growth
Economic growth is an increase in the value of goods and services produced in a country over time. The value of goods and services is the total price of all goods/services multiplied by the total amount produced, in a time period. This is also known as Gross Domestic Product. Therefore, when our GDP increases, we get economic growth.
Reasons why economic growth is desirable
2. Low and Stable Inflation
Inflation is the continuous increase in price levels in an economy in a certain time period. Governments like to have a target of 2-3% inflation in a year.
Reasons why low and stable inflation is desirable
3. Balance of Payments stability
The Balance of Payments are a record of all flows of money made from international trade for a country. It is broken down into three sections (the current account, the capital account and the financial account). The current account records the value of all exports - the value of all imports. If the value of exports is greater than the value of imports then there is a trade surplus but if the value of imports exceeds the value of exports then there is a trade deficit
Reasons why a stable Balance of Payments is desirable
4. Income Equality
Income equality refers to the gap in earnings between the richest and poorest members of society. It can be measured in terms of income earned or as a percentage. It is usually achieved through a fair taxation system.
Reasons why a income equality is desirable
The Business Cycle
This attempts to show fluctuations in real GDP over time. Economists generally predict rising GDP over time (this is known as a trend , but sometimes we achieve above or below our estimated figures.
When GDP is increasing, we enter into a boom . During this period, jobs are increasing, people are spending money and money is entering the economy. This does not last forever though. The highest point during a recovery or boom is a peak .
After this, for various reasons, unemployment starts to rise and people begin to spend less money. As a result incomes fall and we enter a recession . A long recession may also be knnown as a slump . The bottom of a recession is known as a trough .
The distance between two peaks or two troughs is known as an economic cycle , hence the title trade cycle diagram .
The video to the right further illustrates how trade cycle diagrams can be constructed and used.

Government tools
The government may use two types of tools to achieve its aims. These are known as Demand-side policies and Supply-side policies . Demand-side policies attempt to get or stop people spending in an economy, whilst supply side policies aim to encourage or reduce production. We can look at these further, below.
Demand-side Policies
These can be broken down into two types:
How fiscal policy affects business activity
How interest rates affects business activity
Supply-side Policies
These can be broken down into two types:
How taxes affects business activity
Taxes can either be direct (on income, profits or wealth) or indirect (on spending, like VAT, customs duties and excise duties).
Business and the Environment
Businesses have a direct effect on the environment around them, and likewise the environment effects them. Global warming causes problems for farmers and tourism, whilst extreme temperature changes may change spending habits. It is neccessary, therefore for businesses to treat the environment with respect by being sustainable. Sustainable development involves meeting the needs and wants of the present generation without compromising those of future generations. This therefore means trying to do more with less. There are several ways we can do this:
Tasks
http://inhabitat.com/6-inspiring-examples-of-groundbreaking-green-technology/
http://inhabitat.com/top-6-recycling-and-reuse-initiatives-from-around-the-globe/
http://listverse.com/2009/05/01/top-10-renewable-energy-sources/
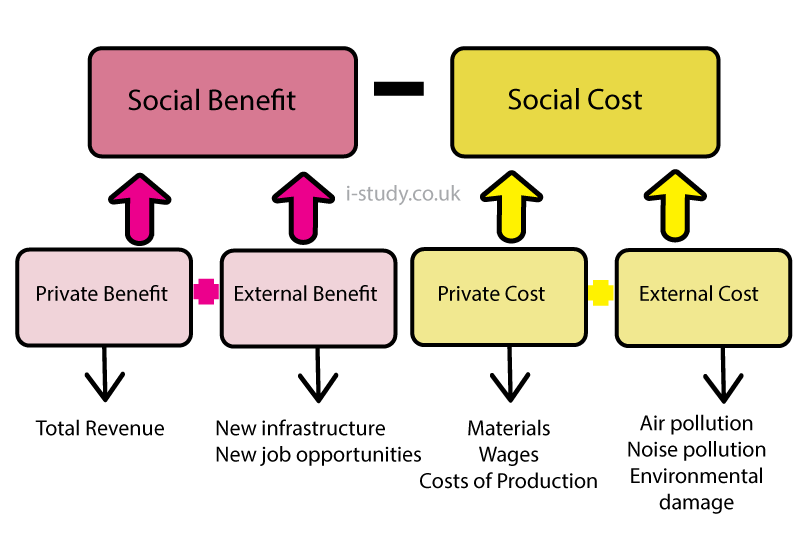
Nevertheless, businesses will always have an effect on the environment. We can calculate how beneficial or how costly a business is to society. We do this through the following equation:
If Social Benefit is greater than Social Costs then the business is good for society and we want it to set up. If Social Benefit is less than Social Costs then the business is not good for society and we do not want it to set up.
But what is social benefit? Social benefit is how much everyone in society - Producers AND Consumers - are better off by the presence of a company. We can therefore break social benefit down into two componants: Private Benefit (the revenue that the producer gets) and External Benefit (the value that consumers are better off by through the actions of the firm). For example:
Similarly, we must break down Social Costs. Social costs are how much everyone in society - Producers AND Consumers - are better off by when a company is at work. We can therefore break social cost down into two componants: Private Cost (the costs the producer pays e.g. materials) and External Costs (the value that consumers are worse off by through the actions of the firm). For example:
In this example above Social Benefit = $170 000 and Social Cost = $70 000 so we can clearly see that overall, this company benefits society by $100 000 ($170 000 - $70 000). The company is therefore valuable for society

Pressure Groups and Environmental Laws
Case Study: Paua New Guinea Rainforest destruction & sustainability Tasks Use the following links to put together a case study; 1 page maximum: include; Map locating Papua New Guinea Brief summary of the problems the country faces & some of the effects they are having. Schemes or efforts to make the country/operations more sustainable. Conclusion - are these schemes having much sucess. Links http://geographyfieldwork.com/TropicalRainforestCaseStudy.htm Papua New Guinea - Case Study revision notes http://coolgeography.co.uk - Papua New Guinea Main page Extract from a report on achieving sustainablility in Papua New Guinea Guardian 2012 - video about the problems in Papua Guardian article supporting the video above
River profile & characteristics: upper, middle & lower valley. Bradshaw model. Waterfalls. River discharge: define, measurement (cumecs).
Ethical issues a business might face; conflicts between profits and ethics • How business might react and respond to ethical issues, e.g. child labour
Pakistan Floods 2010
Flooding is the most obvious and devastating hazard of living close to rivers. Pakistan experienced severe flooding in 2010 that displaced millions of people.
Tasks

Globalisation
Tasks
Watch the video and answer the following questions
Responses to globalisation
Protectionism involves governments attempting to reduce imports (goods being bought from abroad) or increase exports (goods being sold to other countries). There are several ways this could be done.
Tasks
Reasons for Multinationals
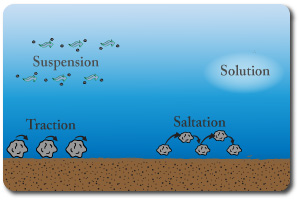
You should be able to explain where these erosional processes take place eg: attrition and abrasion occur largely in the upper course where the larger more angular rocks scrape and collide when they move.
Advantages to Host Country of Multinationals
You should be able to describe the changes in the typeof transportation that occur with distance from the source.
Disadvantages to Host Country of Multinationals