

Needs and Wants
Needs are things that are essential to human survival. These are:
Wants are things that are desired but are not essential for human survival.
The Basic Economic Problem
The basic economic problem is that our needs and wants are infinite but our resources are scarce. This means that we want more than we are actually ever able to make in the long run. We will continue to want consumer goods (like ipads and iphones) for ever but our resources to make these goods (iron, raw materials etc) will run out

Scarcity and Choice
Scarcity refers to the fact that things are limited or finite in nature. If you drink a coca-cola, it is used up, you cannot drink that same cola again. Similarly, if you decide to use some coal to fire a power station, you cannot use that same coal again.
Because resources are scarce we have to make choices about what to produce. This is known as resource allocation. As individuals we make choices according to what gives us the greatest satisfaction. As firms, we decide what to produce according to what gives us the greatest profit. Resources are therefore allocated according to what is most profitable, which in turn relies on consumers feeling satisfied by this product.
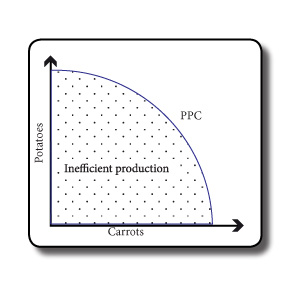
We can illustrate these choices on a Production Possibility Curve (Figure 1.2)- this shows us all the different combinations our resources can be allocated in. If we just produce carrots, we produce no potatoes, and vice versa.
Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative given up when a decision is made. Because resources are scarce we have to make choices over what to produce - we cannot turn a lump of iron into both a chair AND a toy race car, we have to decide between them.
Because we are profit maximizers , we allocate resources according to what is most profitable. If we are set to make $50m from choosing to make chairs rather than $40m from toy race cars, we go for the chairs. Our opportunity cost is therefore $40m; we gave up the possibility of making $40m in order to make $50m. Every choice a firm takes has an opportunity cost.
Specialisation
Specialisation is the process of increasing efficiency by becoming a master of a specific area. Because resources are scarce, it is vital that we waste as little as possible when producing. By wasting little, we can produce more, and therefore earn greater profits. Specialisation allows for greater productivity. It can be achieved through
Advantages / Disadvantages of Specialisation
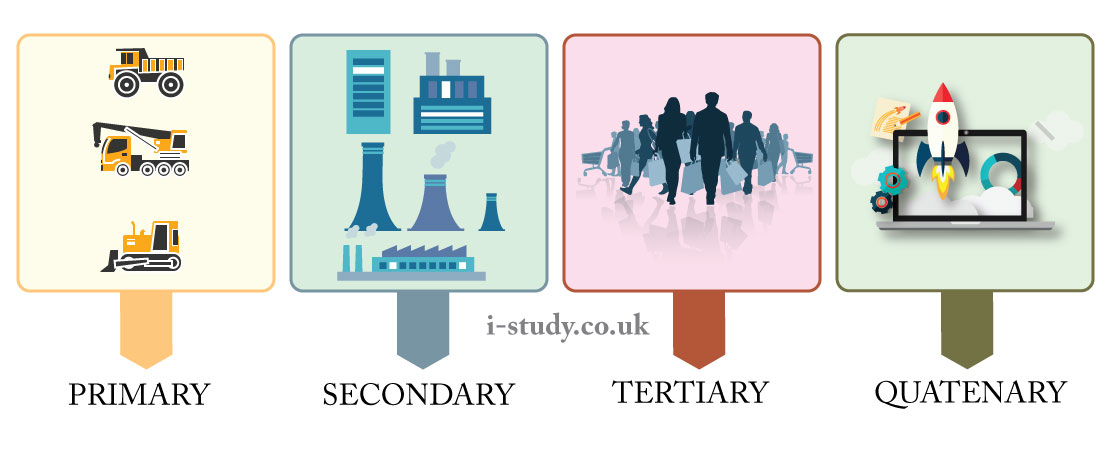
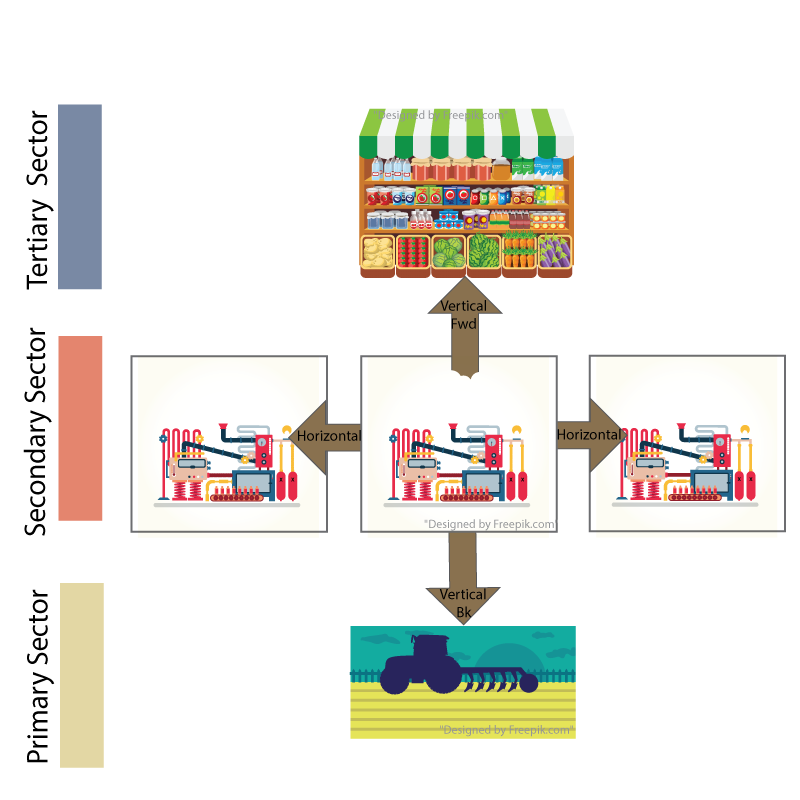
Industrial Classifications
In any country, we can catagorize production into three or four main industries:
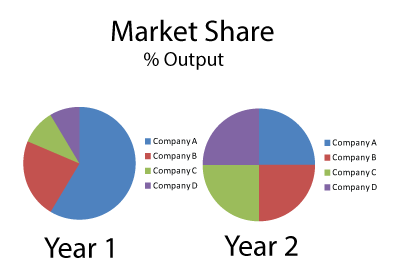
Look at the pie chart below then answer the questions. It shows the percentages of the value of output produced in an economy by sector
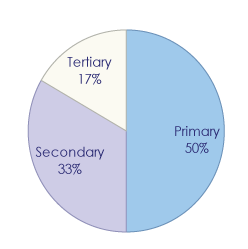
1) If the primary sector were to decrease, how might this be evidence of development?
2) Is there a relationship between the size of a sector and the level of employment in that sector?
3) In which sector would you find the most value-added products?
Economic Classifications
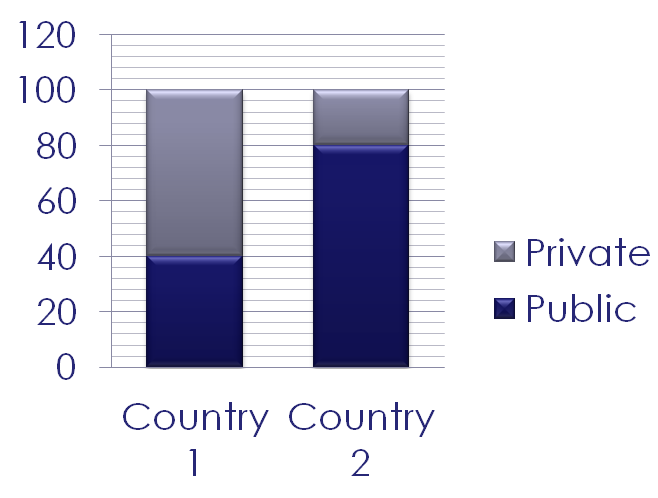
Economic Sectors can be split into two areas; the public and the private.
In a command economy, the government owns all the resources of a country, so only the public sector exists, not the privat
In a free market economy, there is no government, and all resources are owned by individuals in the private sector.
Most economies are a mix of both sectors and are therefore known as mixed economies
Importance of Economic Classifications:
Look at the pie chart to the right, which shows economic sectors by output:

Entrepreneurs
Characteristics of successful entrepreneurs are of particular interest to people with businesses.
Read the following article and answer the questions below:
http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-33068445
1) Using examples from the article, give three characteristics you would use to describe Mr Altrad
2) Use an example to show how Mr Altrad responded to adversity
3) What do you think motivates Mr Altrad? Use a quote from the text to prove your point
4) How do you think Mr Altrad's experiences helped shape him for the world of business? Use quotations from the text to explain your answer.
Business Plans
What is a business plan?This is a document that records a wide variety of information neccessary to the new entrepreneur. It will include information on:
a) The nature of the product
b) The market
c) The competition
d) Finances
Why are business plans important?

The Role of the Government
How government's help start-ups and SMEs
An SME is a small or medium enterprise. These are often known as start-ups when they are first set up. The government often helps them through
Why do governments help start-ups?
Size and Growth
Measuring Business Size
How to measure business size:
Each of the above measurements, however, will give different companies different sizes.
How businesses can grow
Types of Integration
Benefits of Integration
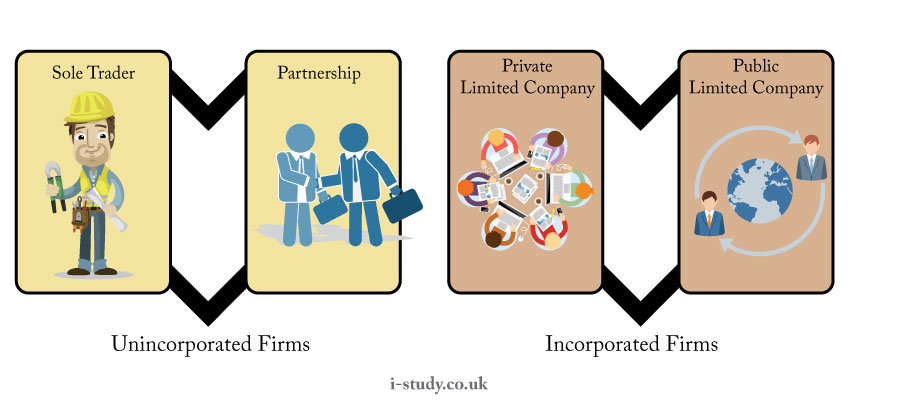
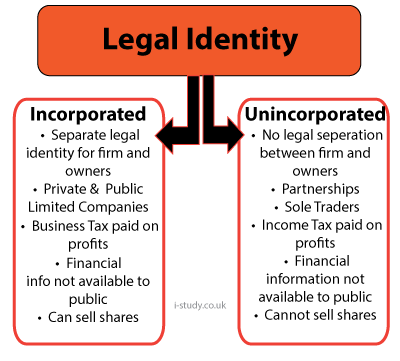
| Form | Features | Advantage | Disadvantage |
| Sole Trader |
|
|
|
Paternership
|
|
|
|
| Private Limited |
|
|
|
| Public Limited |
|
|
|
| Joint Venture |
|
|
|
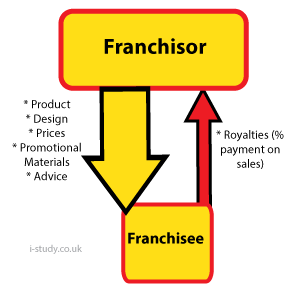
Franchises
This is when an established company (usually a multinational) provides an entrepreneur with the right to sell the established company's products. The franchisor (the established company) provides a lot of the materials needed for doign so, such as packaging, design, prices and advice, and the franchisee (the new company) then sells these products for the franchisor. In return, the franchisee pays a royalty back to the partent company - this is usually a % of the profits earned.
Public Sector Organisations
We can identify two different public sector organisations:
Read the following article:
Business Objectives
Read the following article and then answer the questions:
http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/technology-33534256
1) What have Amazon's profits traditionally been like?
2) Using figures, explain what objective has Amazon put before profit?
3) How is it possible for one firm to have lower revenues and higher profits than another?
4) What does Amazon do with a lot of the profit it generates?
5) Give some examples of innovations that may not yet be profitable that Amazon has created.
6) How much revenue did Amazon make in 2015?
Business Objectives over time
The objectives of a firm depend upon the environment it is operating in. If just starting out, an SME might make survival its main objective. After that, it may wish to expand the business before focusing on profit. Alternatively, if there is a downturn in the economy then a firm may stop trying to grow and focus on profit instead. The situation a firm is in therefore influences its objectives.

Social Enterprises
These are companies that do not necessarily have profit as their main objective. Instead they may aim to have a variety of social or ethical aims such as:
Stakeholders
Stakeholders are groups or individuals that have an interest in the success of a business. All stakeholders want the company to succeed but may also have other objectives.
Internal stakeholders are those that can be found within the company. They include:
External stakeholders are those that are found outside of the company. They include:
Stakeholder Conflict ocurs when two or more stakeholders groups want things that are opposed to one another. Fill in the table below outlinging how the groups may conflict. Examples may include the local community being upset about a manager's decision to lay off workers in order to make more profit. Fill in the Table to show how they may conflict
| Government | Local Community | Suppliers | |
Employer
|
|||
Managers
|
|||
Shareholders
|
|||
Owners
|